Scout missions
Scout missions can prove new concepts using small satellites, which can then be scaled up in larger missions.
- From:
- UK Space Agency
- Published
- 27 April 2022
- Last updated
- 6 November 2025 — See all updates


Credit:
CubeMAP consortium
ESA
The Scout missions are aan new element inof ESA’s Earth Observation Programme.
Theprogramme ideathat isdemonstrate toinnovative provescience new concepts using small satellites developed in a fast, agile manner,small whichsatellites, addenabling scientificfast valuedeployment toand datavalidation fromof currentnew satellites.technologies.
The concepts can then be scaled up in larger missions.
The UK hasis wonleading the competitiondevelopment toof build and deliver the first twoScout missions,mission, whichHydroGNSS, makesleveraging usenational of our strengths in building small satellitessatellite engineering and ourEarth scientificObservation expertise.science. TheseScheduled missionsfor seeklaunch toin deliverlate vital2025 newwith informationSpaceX, aboutHydroGNSS ourwill support climate monitoring and environmentenvironmental inresilience aby new,delivering faster,vital cheaperdata way.
Bothmore missionsquickly areand due for launch at the end of 2024.cost-effectively.
Scout Mission: CubeMAPHydroGNSS
Key features
TheHydroGNSS is Scoutthe CubeMAPfirst missionESA willScout bemission, aled constellationby ofthe multipleUK separateand CubeSats.
Itsbuilt goalby isSSTL, tolaunching study,November understand,2025. andIt quantifywill processesuse insmall thesatellites tropical upper troposphere and stratosphereGNSS-Reflectometry (UTS),to particularlydeliver inrapid, theaffordable contextmeasurements of climatekey changehydrological andclimate increasedvariables such emissionsas insoil themoisture, tropics.permafrost, Theinundation, missionbiomass, willwind providespeed, insightsand onsea theice compositionextent - supporting ongoing ofclimate thescience, UTS,environmental studyresilience, its variability, and itsfuture effectsscalable on climate and vice-versa.constellations.
InScout particular,missions thecan constellationprove willnew makeEarth observationsObservation inconcepts tropicalusing andsmall sub-tropicalsatellites, latitudeswhich tocan observethen aerosolsbe andscaled gasesup suchin as:
waterlargervapourcarbonmissions.dioxidemethanenitrousTheseoxide
Allare ofa component of thesethe playEuropean aSpace keyAgency’s roleEarth inObservation theFuture greenhouseEO effect and climate change.programme.
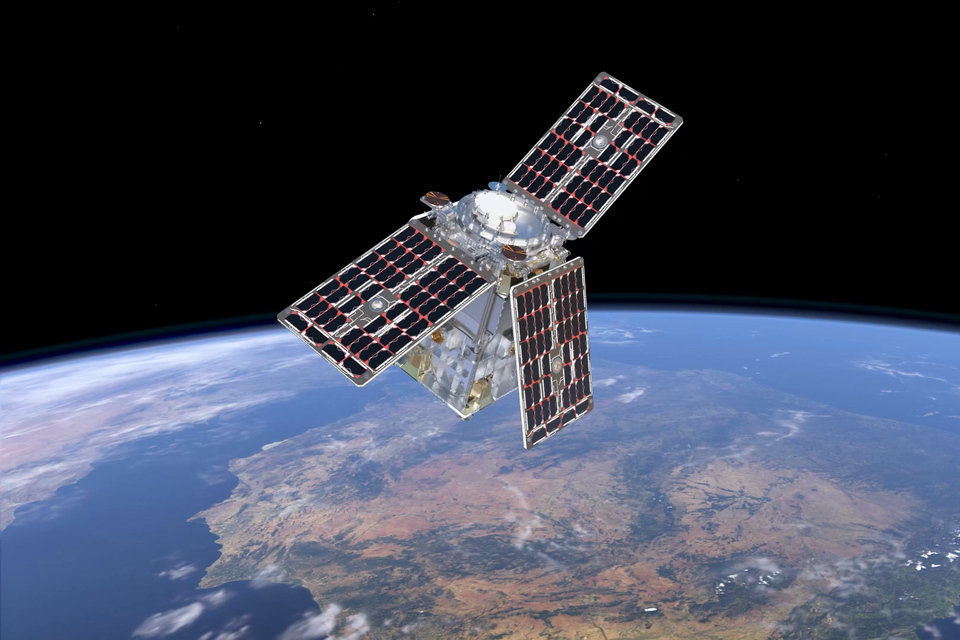

TheArtist's missionimpression isof packedHydroGNSS within noveltyorbit. andCredit: innovation:ESA/ATG aMedialab.
Key novelfeatures
- Mission:
conceptHydroGNSSofmeasurementfromaconstellationusedtoprofileatmosphere,firstforESAwhichScoutthemission,sun,designedthetoatmospheremeasureandhydrologicaltheclimatesatellitevariablesareusingaligned;smallandsatellites. - Launch:
newinstrumenttechnologiesenableminiaturisationandtheuseofnanosatellites.The mission
comprisesisthreescheduled12-litretocubesats,launcheachincarryingNovemberthermal2025,infraredonspectrometers,aswellasvisibleSpaceXnear-infraredrocket. - Instrument:
hyperspectralHydroGNSSsolarusesdiskGNSS-Reflectometryimagertoasremotelyasensesecondarysoilinstrument.UKmoisture,involvementThepermafrost,UKinundation,isbiomass,thewindinitiatorspeed, andtheseascientificiceandextent. - Accuracy:
payloadHydroGNSSleadisofdesignedthetomission.deliverWithclimatethedatacontractwithnowasigned,sensitivityGomSpaceofin0.7–3.8DenmarkdBwillperlead10%anchangeindustrialinconsortiumgeophysicaltoparametersbuildandCubeMAP.aThespatialconsortiumresolutionincludesofRutherford2–7Appletonkm. - Mission
LaboratoryLife:(RAL)PlannedinoperationalthelifeUK,ofGomSpacethreeinyearsLuxembourginpossibleSweden,extensionEnpulsionupintoAustria,fiveHyperionorinsixtheyears - UK
NetherlandsRole:andTheKongsbergUKSatelliteleadsServicesthe(KSAT)mission,inwithNorway.ScoutSSTLMission:designing,HydroGNSSWithbuilding,fundingandfromoperatingESA’stheScoutsatellites,programme,supportedSurreybySatellitenationalTechnologyandLtdEuropean(SSTL)isbuildingHydroGNSS,a55kgsmallsatellitetomeasureclimatechangevariables.partners.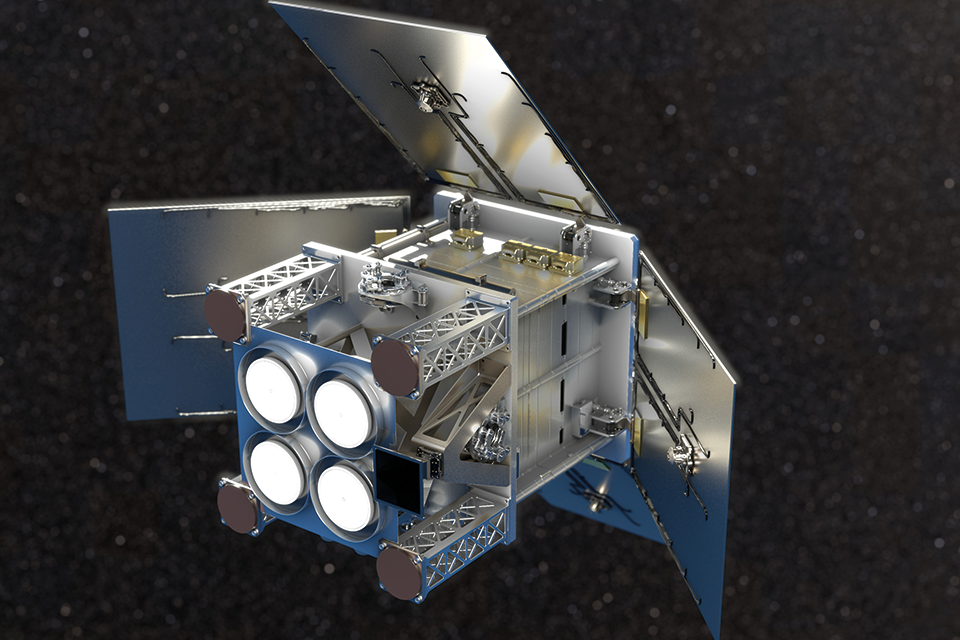
Credit: SSTL
Key features
The HydroGNSS satelliteScout-class willmission takeconsists measurements of keytwo hydrologicalsatellites. climate variables, using a technique called GNSS Reflectometry, including:
soilmoisture,freezethawstateoverpermafrost,inundationandwetlands,andabovegroundbiomass
The purpose is to measure parameters directly linked to Essential Climate Variables (ECV)(ECVs) - key indicators that are used to describe the Earth’s changing climate on a global scale. Collectively, there are 5455 ECVs which provide empirical evidence to support climate science and better predict future change. Of these, around 60% can be addressed by satellite data.
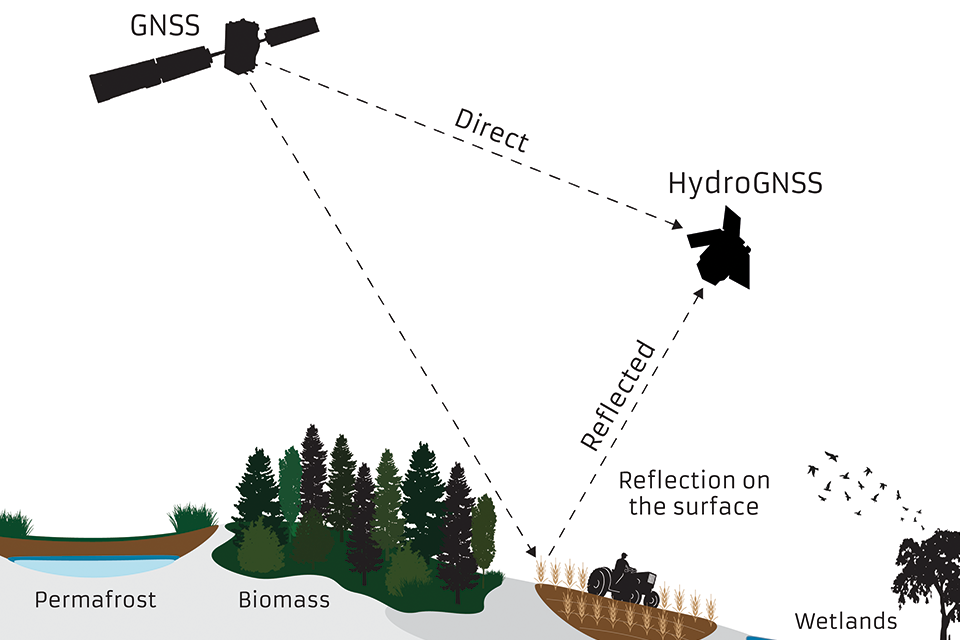
ECVsUsing are specified by the Global ClimateNavigation ObservingSatellite System,System aReflectometry system(GNSS-R), thatHydroGNSS compriseswill theremotely climate-relevantsense componentshydrological ofclimate manyvariables contributingincluding observingsoil systemsmoisture, andpermafrost networks.
Knowledgefreeze-thaw ofstate, theseinundation, variablesabove-ground helpsforest scientistsbiomass, understandand climatewind changespeed andover the dataocean isand asea valuableice toolextent.
These formeasurements manysupport applicationsclimate includingand weather modelling, ecology mapping, agricultural planningplanning, and flood preparedness.
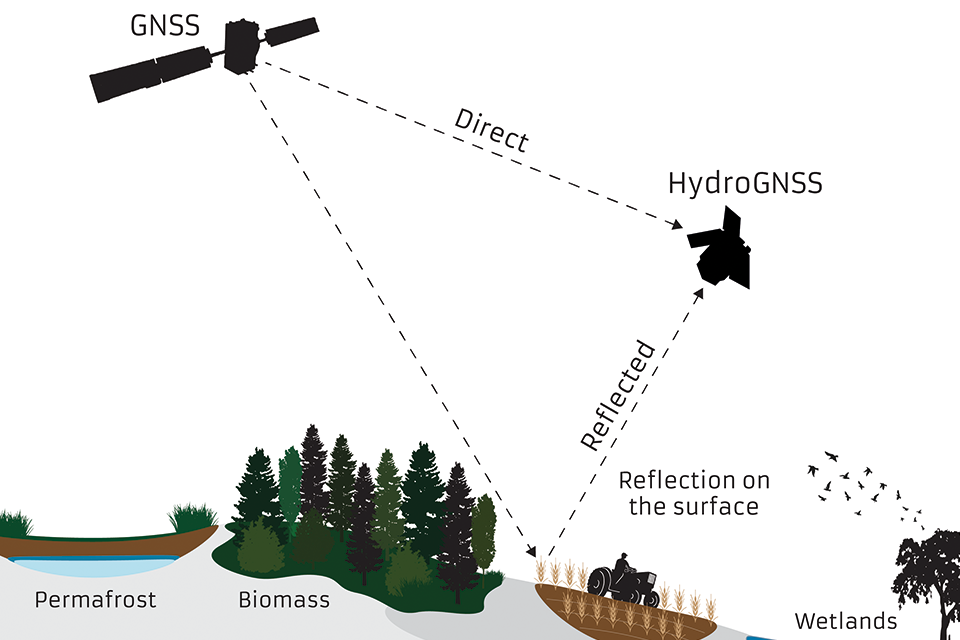
GlobalDiagram: NavigationGNSS Satellitesatellite Systemsignal (GNSS)direct Reflectometryand isreflected ato techniqueHydroGNSS wherebysatellite, signalsstudying frompermafrost, GPSbiomass, soil moisture and wetlands.
The two satellites reflectedweigh offaround the65kg land,each, icesimilar andin oceanmass and cansize beto collecteda byhousehold awashing low-powermachine. receiverThe onmission ais smallfunded satelliteby inESA’s low-EarthScout orbit,programme and usedprogress to yielddate importantfollows geophysicalearly-stage measurements.
Credit:development SSTLfunding via the UK’s Centre for Earth Observation Instrumentation to accelerate the maturation of critical technologies.
HydroGNSS paves the way for an affordable future constellation that can offer much more frequent, responsive measurements than is possible with traditional remote sensing satellite systems,systems. offeringThis offers a new ability to monitor very dynamic phenomenaphenomena, such as diurnal soil moisture changes and freeze and thaw cycles of permafrostpermafrost, and helpinghelps to fill the gaps in our monitoring of the Earth’s vital signs for the future.
UK involvement
Funded by the UK Space Agency with £26 million and the European Space Agency. Led by Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd (SSTL), working closely with partners at Sapienza, Tor Vergata and IFAC-CNR in Italy, FMI in Finland, IEC/IEECICE/IEEC in Spain, National Oceanographic Centre (NOC) in UK, and University of Nottingham to tackle the scientific and technological challenges involved. The mission and satellite are designed, built and operated in the UK by Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd.
CubeMAP
Key features
The Scout CubeMAP mission will be a constellation of multiple separate CubeSats.
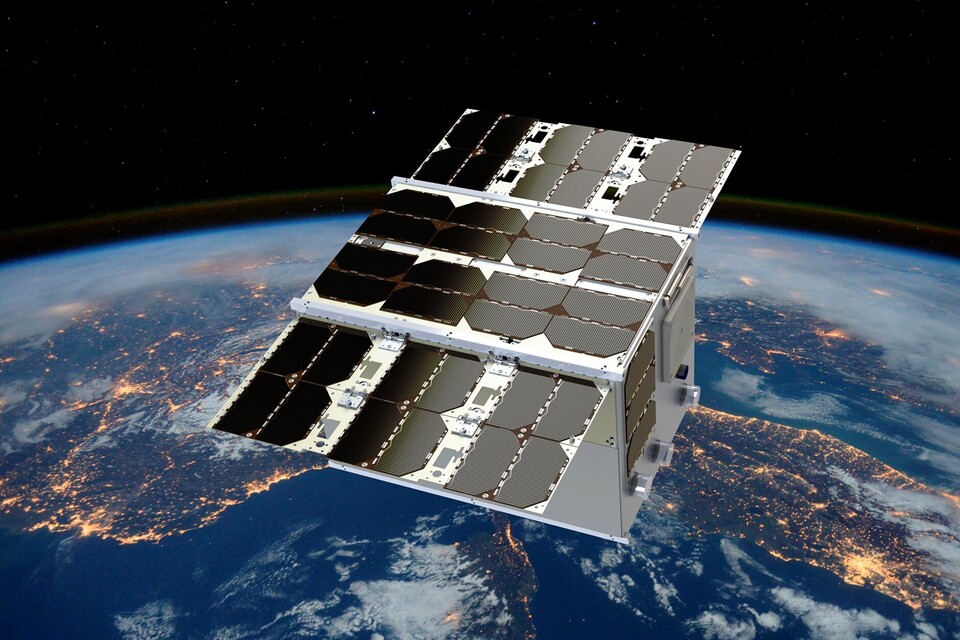

Artist's impression of CubeMAP in orbit. Credit: CubeMAP consortium
Its goal is to study, understand, and quantify processes in the tropical upper troposphere and stratosphere (UTS), particularly in the context of climate change and increased emissions in the tropics. The mission will provide insights on the composition of the UTS, study its variability, and its effects on climate and vice-versa.
In particular, the constellation will make observations in tropical and sub-tropical latitudes to observe aerosols and gases such as:
- water vapour
- carbon dioxide
- methane
- nitrous oxide
All of these play a key role in the greenhouse effect and climate change.
The mission is packed with novelty and innovation: a novel concept of measurement from a constellation is used to profile the atmosphere, for which the sun, the atmosphere and the satellite are aligned; and new instrument technologies enable miniaturisation and the use of nanosatellites.
The mission comprises three 12-litre cubesats, each carrying thermal infrared spectrometers, as well as a visible near-infrared hyperspectral solar disk imager as a secondary instrument.
UK involvement
The UK is the initiator and the scientific and payload lead of the mission. With the contract now signed, GomSpace in Denmark will lead an industrial consortium to build CubeMAP. The consortium includes Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (RAL) in the UK, GomSpace in Luxembourg and in Sweden, Enpulsion in Austria, Hyperion in the Netherlands and Kongsberg Satellite Services (KSAT) in Norway.
Updates to this page
-
Updated HydroGNSS content.
-
First published.