Democratic Republic of the Congo
Summary
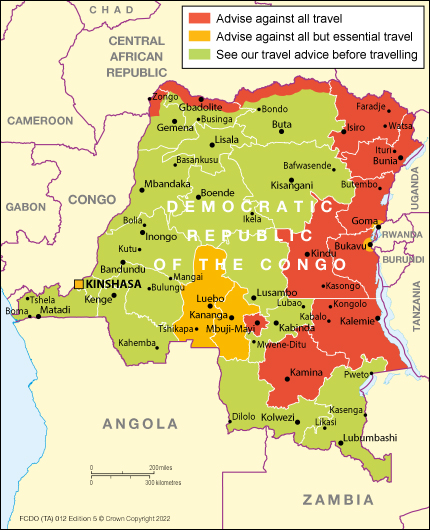
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO) advises against all travel to:
- the provinces of Kasaï Oriental, Haut-Uele, Haut Lomami, Ituri, North Kivu (except the city of Goma), South Kivu (except the city of Bukavu - see below), Maniema and Tanganyika in eastern DRC
areastothewestandeastofKananga,includingTshikapaandMwene-Ditu(asshownonthemap)- within 50km of the border with the Central African Republic and South Sudan
The FCDO advises against all but essential travel to:
- the city of Goma in North Kivu province
- the city of Bukavu in South Kivu province
- the districts of N’djili and Kimbanseke in Kinshasa, both of which are south of the main access road to N’djili airport (located in Nsele district)
- the provinces of Kasiaï and Kasiaï Central
If you are a foreign national resident in the city of Kinshasa, you must renew your residency card at the provincial commission by 15 July. The local government has said that people who do not meet the deadline will have to pay an additional fine.
COVID-19 entry restrictions for Democratic Republic of the Congo
Before you travel, check the ‘Entry requirements’ section for Democratic Republic of the Congo’s current entry restrictions and requirements. These may change with little warning. Monitor this advice for the latest updates and stay in contact with your travel provider.
Travelling from and returning to the UK
Check what you must do to travel abroad and return to England, Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland.
If you plan to pass through another country to return to the UK, check the travel advice for the country you’re transiting.
If you’re planning travel to the Democratic Republic of Congo, find out what you need to know about coronavirus there in the Coronavirus section.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, it is more important than ever to get travel insurance and check it provides sufficient cover. See the FCDO’s guidance on foreign travel insurance.
For information about COVID-19 vaccines, see the Coronavirus page.
On 22 August 2022 DRC declared a new Ebola outbreak in Beni, North Kivu province in eastern DRC. Further information and updates on Ebola can be found on the WHO website and the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) website. UKHSA has guidance for humanitarian or healthcare workers travelling to an Ebola affected area. See Health.
Further protests may take place in and around Goma, North Kivu province from 5 August 2022. These could be directed at UN personnel and others within the international community. We advise all UK nationals in DRC to remain vigilant at this time and to avoid demonstrations, protests or disturbances.
On 25 July 2022, demonstrations began in and around Goma, North Kivu province, spreading to other areas in eastern DRC, including Butembo, Sake, Beni, and Uvira, including reports of violence against United Nations facilities and personnel. There is an increased presence of security forces in and around Goma and in affected areas across eastern DRC. You should exercise caution in travel in the city of Goma and avoid crowds and demonstrations. FCDO staff may leave the area temporarily at short notice. See Protests and demonstrations
On 4 July 2022 DRC’s 14th Ebola outbreak was declared over. The outbreak began on 23 April 2022 in Mbandaka City, Equateur province in Northern DRC. There have been no new cases since 19 May 2022. Further information and updates on Ebola can be found on the WHO website and the Public Health England (PHE) website. Public Health England has guidance for humanitarian or healthcare workers travelling to countries at risk of Ebola. See Health
On 22 May 2021, Mount Nyiragongo volcano, close to the city of Goma, and near the border with Rwanda erupted. Further volcanic activity is possible in future. See Natural disasters and Safety and security
On 12 May 2022 reports were received indicating the risk of a terrorist attack on an unspecified ferry departing from Goma. The UK advises against all but essential travel to Goma.
The Embassy is not currently open to external visitors. It continues to carry out essential work including providing 24/7 consular assistance and support to British people in DRC.
Public gatherings and demonstrations can occur with little or no notice and can quickly turn violent. See Political situation
The security situation in eastern DRC remains unstable. There are continued reports of attacks and kidnappings. NGO staff have been known to be targeted. A “state of siege” is in place in the provinces of Ituri and North Kivu. Military administrations have replaced the civilian administrations during this period. Military forces from DRC and Uganda began conducting air and artillery raids against the Allied Defence Force (ADF) in eastern DRC on 30 November. Ugandan troops are also present as part of joint operations. See Safety and security
Consular support is severely limited in parts of DRC. The lack of infrastructure throughout the country and insecurity in eastern DRC often prevent the British Embassy in Kinshasa from being able to extend normal levels of consular assistance to British nationals anywhere in the DRC other than Kinshasa. You should not assume that the FCDO will be able to provide assistance to leave the country in the event of serious unrest or crisis.
Street crime and robbery is common. You should avoid using any taxis in DRC. If you must take a taxi, use a privately booked one. Don’t hail taxis in the street. Beware of gangs promising you cut price gold and diamonds. See Crime
Terrorists are very likely to try to carry out attacks in the DRC. Attacks could be indiscriminate. You should be vigilant, especially in places visited by foreigners. See Terrorism
On 25 July 2022, demonstrations began in Goma, North Kivu province, including reports of violence against United Nations facilities and personnel. You should exercise caution in travel in the city of Goma and avoid crowds and demonstrations. FCDO staff may leave the area temporarily at short notice.
If you’re abroad and you need emergency help from the UK government, contact the nearest British embassy, consulate or high commission.